This guide helps you create a Java full stack application with all the CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) features using React as Frontend framework and Spring Boot as the backend REST API. We will be using JavaScript as the frontend language and Java as the backend language.
You will learn
- What is a full stack application?
- Why do we create full stack applications?
- How do you use React as a Frontend Framework?
- How do you use Spring to create Backend REST Service API?
- How do you call Spring Boot REST API from React using the axios framework?
- How and When to use different REST API Request Methods - GET, POST, PUT and DELETE?
- How do you perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) operations using React as Frontend framework and Spring Boot as the backend REST API?
- How do you create a form in React using Formik?
Step 0: Get an overview of the Full Stack Application
Understanding Basic Features of the Application
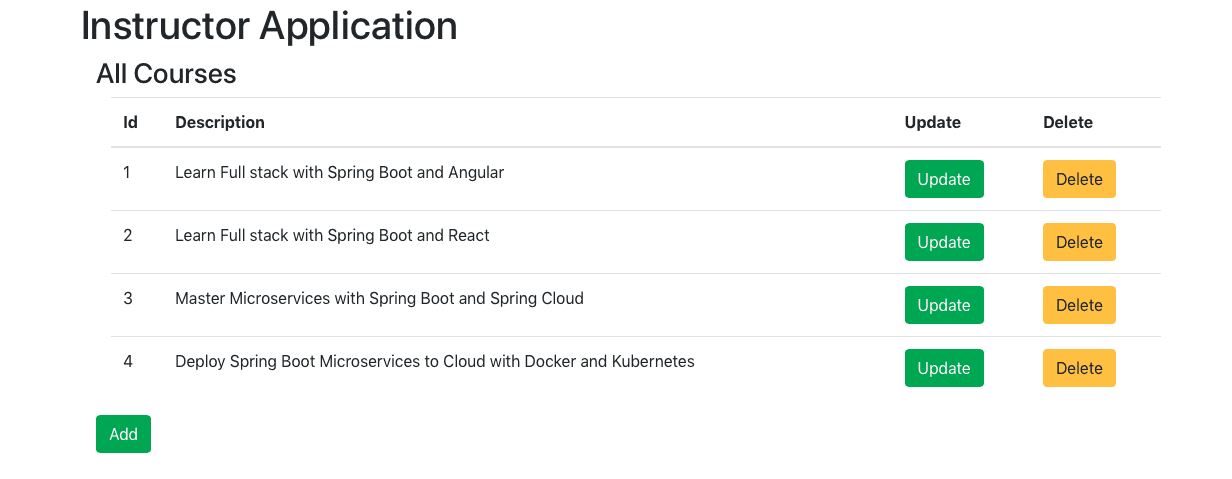
Following screenshot shows the application we would like to build:
It is a primary instructor portal allowing instructors to maintain their courses.

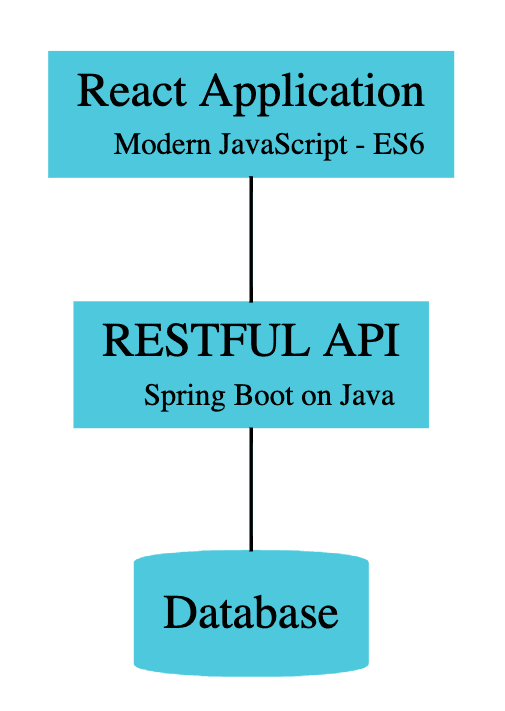
Understanding Full Stack Architecture
Following Screenshot shows the architecture of the application we would create:

Important points to note:
- REST API is exposed using Spring Boot
- REST API is consumed from React Frontend to present the UI
- The Database, in this example, is a hardcoded in-memory static list.
You can find more details about Full Stack Architecture here - Full Stack Application Architecture - Spring Boot and React
Getting an overview of Spring Boot REST API Resources
In this guide, we will create these services using proper URIs and HTTP methods:
@GetMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses"): Get Request Method exposing the list of courses taught by a specific instructor@GetMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses/{id}"): Get Request Method exposing the details of a specific course taught by a specific instructor@DeleteMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses/{id}"): Delete Request Method to delete a course belonging to a specific instructor@PutMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses/{id}"): Put Request Method to update the course details of a specific course taught by a specific instructor@PostMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses"): Post Request Method to create a new course for a specific instructor
The REST API can be enhanced to interact with other microservices infrastructure components and act as microservices.
Downloading the Complete Maven Project With Code Examples
Following GitHub repository hosts the complete frontend and backend projects - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-react-fullstack-examples/tree/master/spring-boot-react-crud-full-stack-with-maven
Our Github repository has all the code examples - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-react-examples/
Understanding Spring Boot REST API Project Structure
Following screenshot shows the structure of the Spring Boot project we create.
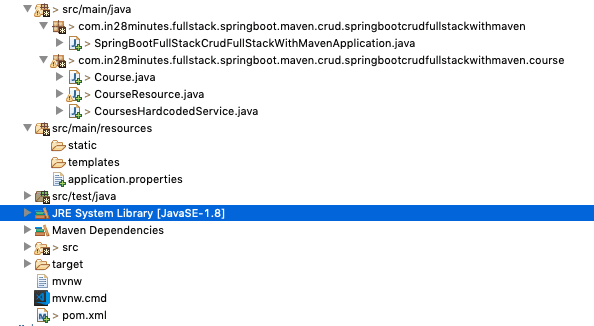
A few details:
CourseResource.java- Rest Resource exposing all the service methods discussed above.Course.java, CoursesHardcodedService.java- Business Logic for the application. CoursesHardcodedService exposes a few methods we would invoke from our Rest Resource.SpringBootFullStackCrudFullStackWithMavenApplication.java- Launcher for the Spring Boot Application. To run the application, launch this file as Java Application.pom.xml- Contains all the dependencies needed to build this project. We use Spring Boot Starter Web and Spring Boot DevTools.
Understanding React Frontend Project Structure
Following screenshot shows the structure of the React project we create.
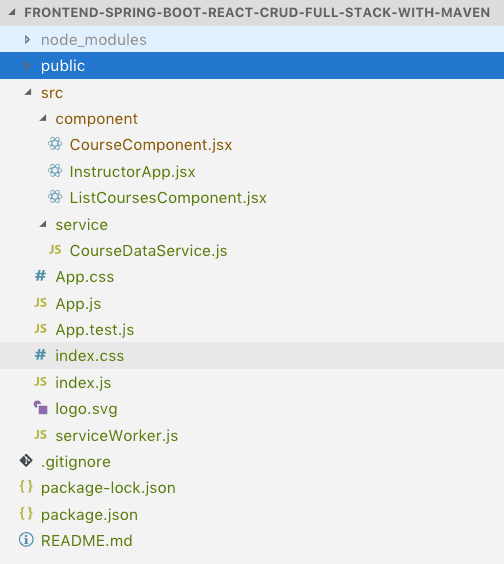
Quick Tip: You can get a high-level overview of all files in the React Project Structure watching this video React Project Structure
A few details:
InstructorApp.jsx: React Component representing the high-level structure of the application. Routing is defined in this file.ListCoursesComponent.jsx- React Component for listing all the courses for an instructor.CourseComponent.jsx- React Component for editing Course Details and creating a new courseCourseDataService.js- Service using axios framework to make the Backend REST API Calls.
Understanding the tools you need to build this project
- Maven 3.0+ for building Spring Boot API Project
- npm, webpack for building frontend
- Your favorite IDE. We use Eclipse for Java and Visual Studio Code for Frontend - JavaScript, TypeScript, Angular and React.
- JDK 1.8+
- Node v8+
- Embedded Tomcat, built into Spring Boot Starter Web
Installing Node Js (npm) & Visual Studio Code
- Playlist - [Click to see video Playlist](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLBBog2r6uMCQN4X3Aa_jM9qVjgMCHMWx6
- Steps){:target=”_blank”}
- Step 01 - Installing NodeJs and NPM - Node Package Manager
- Step 02 - Quick Introduction to NPM
- Step 03 - Installing Visual Studio Code - Front End JavaScript Editor
Installing Java, Eclipse & Embedded Maven
- Playlist - [Click to see video Playlist](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLBBog2r6uMCSmMVTW_QmDLyASBvovyAO3
- Steps){:target=”_blank”}
- 0 - Overview - Installation Java, Eclipse and Maven
- 1 - Installing Java JDK
- 2 - Installing Eclipse IDE
- 3 - Using Embedded Maven in Eclipse
- 4 - Troubleshooting Java, Eclipse and Maven
Creating Full Stack CRUD application with React and Spring Boot - Step By Step Approach
We will use a step by step approach to creating the full stack application
- Create a Spring Boot Application with Spring Boot Initializr
- Create a React application using Create React App
- Create the Retrieve Courses REST API and Enhance the React Front end to retrieve the courses using the axios framework
- Add feature to delete a course in React front end and Spring Boot REST API
- Add functionality to update course details in React front end and Spring Boot REST API
- Add feature to create a course in React front end and Spring Boot REST API
You can get an introduction to REST down here - Introduction to REST API
Step 1: Bootstrapping Spring Boot REST API with Spring Initializr
Creating a REST service with Spring Initializr is a cake walk. We will use Spring Web MVC as our web framework.
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ is great tool to bootstrap your Spring Boot projects.
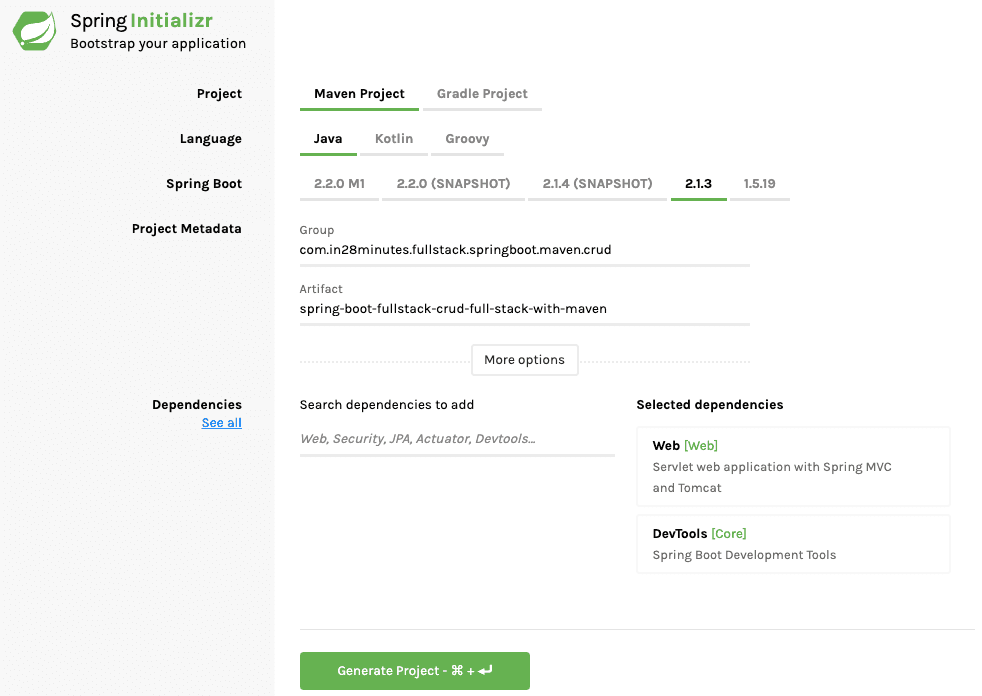
As shown in the image above, the following steps have to be done
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following
- Choose
com.in28minutes.fullstack.springboot.maven.crudas Group - Choose
spring-boot-fullstack-crud-full-stack-with-mavenas Artifact - Choose following dependencies
- Web
- DevTools
- Choose
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the project into Eclipse. File -> Import -> Existing Maven Project. For more details about creating Spring Boot Projects, you can read - Creating Spring Boot Projects
If you are new to Spring Boot, we recommend watching this video - Spring Boot in 10 Steps
Step 2 - Bootstrapping React Frontend with Create React App
Create React App is an amazing tool to bootstrap your React applications.
Creating React Frontend Applications with Create React App is very simple.
Launch up your terminal/command prompt. Make sure that you have node installed.
npx create-react-app frontend-spring-boot-react-crud-full-stack-with-maven
You can find more information about using Create React App here - Create React App - Create and Launch a React Application
You can get a high-level overview of all files in the React Project Structure here - React Project Structure
Launching up React Frontend
You would need to cd to the project we created and execute npm start
cd frontend-spring-boot-react-crud-full-stack-with-maven
npm start
You would see the screen below:
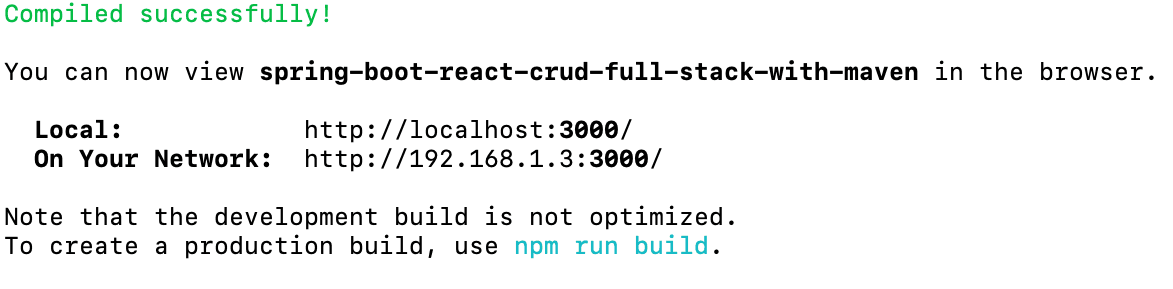
When you launch up the application in the browser at http://localhost:3000/, you would see the following welcome screen.

You can import the created project into Visual Studio Code by using File > Open > Select the project created earlier. You can find more details here - Importing React App into Visual Studio Code
Cool! You are all set to rock and roll with React.
Step 3 - Creating REST API for Retrieve All Courses and Connecting React Frontend
We would want to start building the screen shown below:

Let’s start with building the course listing screen.
To be able to do that, we need to
- Create REST API for retrieving a list of courses.
- Connect the React Frontend to the backend REST API
Create REST API for retrieving a list of courses
Web Services, REST and Designing REST API, are pretty deep concepts. We would recommend to check this out for more - Designing Great REST API
We will create
- A model object
Course.java - A Hardcoded Business Service
CoursesHardcodedService.java - A Resource to expose the REST API
CourseResource.java
We will start with creating a model object Course.java. The snippet below shows the content of the model class. For the complete listing, refer course/Course.java in the complete code example at the end of this article.
public class Course {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String description;
//no arg constructor
//constructor with 3 args
//getters and setters
//hashcode and equals
Next, let’s create a Business Service. In this article, we will use hardcoded data.
@Service
public class CoursesHardcodedService {
private static List<Course> courses = new ArrayList<>();
private static long idCounter = 0;
static {
courses.add(new Course(++idCounter, "in28minutes", "Learn Full stack with Spring Boot and Angular"));
courses.add(new Course(++idCounter, "in28minutes", "Learn Full stack with Spring Boot and React"));
courses.add(new Course(++idCounter, "in28minutes", "Master Microservices with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud"));
courses.add(new Course(++idCounter, "in28minutes",
"Deploy Spring Boot Microservices to Cloud with Docker and Kubernetes"));
}
public List<Course> findAll() {
return courses;
}
}
Few things to note
- Data is hardcoded
- findAll returns the complete list of courses
- You can see that the API of the Service is modelled around the Spring Data Repository interfaces. If you are familiar with JPA and Spring Data, you can easily replace this with a Service talking to a database.
Next, let create the REST Resource to retrieve the list of courses for an instructor.
@RestController
public class CourseResource {
@Autowired
private CoursesHardcodedService courseManagementService;
@GetMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses")
public List<Course> getAllCourses(@PathVariable String username) {
return courseManagementService.findAll();
}
}
Few things to note:
@RestController : Combination of @Controller and @ResponseBody- Beans returned are converted to/from JSON/XML.@Autowired private CoursesHardcodedService courseManagementService- Autowire the CoursesHardcodedService so that we can retrieve details from business service.
If you launch up the Spring boot application and go to http://localhost:8080/instructors/in28minutes/courses in the browser, you would see the response from the API.
[
{
"id": 1,
"username": "in28minutes",
"description": "Learn Full stack with Spring Boot and Angular"
},
{
"id": 2,
"username": "in28minutes",
"description": "Learn Full stack with Spring Boot and React"
},
{
"id": 3,
"username": "in28minutes",
"description": "Master Microservices with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud"
},
{
"id": 4,
"username": "in28minutes",
"description": "Deploy Spring Boot Microservices to Cloud with Docker and Kubernetes"
}
]
We have the REST API up and running. Its time to focus on the Frontend.
Enhancing React App to consume the REST API
To be able to enhance the React Application to consume the REST API, we would need to
- Create an Application Component - to represent the structure of the complete application and include it in
App.jsx-InstructorApp.jsx - Add the frameworks need to call the REST API - axios, display a form - formik and support routing - react-router-dom
- Create a view component for showing a list of course details and include it in the Application Component -
ListCoursesComponent.jsx - Invoking Retrieve Courses REST API from React Component - To enable this we will create a service to call the REST API using the axios framework -
CourseDataService.js.ListCoursesComponent.jsxwill make use ofCourseDataService.js
Let’s start with creating an Application Component - InstructorApp.jsx
/src/component/InstructorApp.jsx
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class InstructorApp extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h1>Instructor Application</h1>
)
}
}
export default InstructorApp
Few things to note:
- One of the first things you would need to understand about React is the concept of the component. You can find more about a react component here - React Components
class InstructorApp extends Component- Every React Class Component should extend a class called Component.render()- The render() method of a component returns what needs to be displayed as part of the componentexport default InstructorApp- Each JavaScript file is a module. If you wanted elements from a JavaScript module to be used in other JavaScript modules, we would need to export them. Here, we are makingInstructorAppavailable for import in other components.
Let’s update the App.js to display the InstructorApp component.
src/App.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import InstructorApp from './component/InstructorApp';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<InstructorApp />
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
Few things to note:
import InstructorApp from './component/InstructorApp'- Importing the InstructorApp component class<InstructorApp />- Display the Instructor App component.
Let’s update the App.css to use Bootstrap framework:
/src/App.css
@import url(https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css)
When you launch the React app in the browser, it will appear as shown below:
Adding Frameworks to React Application
In this project, we will make use of axios to execute REST APIs, react-router-dom to do the Routing between pages and formik to create forms. Let’s stop the front end app running in the command prompt and execute these commands.
npm add axios
npm add react-router-dom
npm add formik
When commands execute successfully, you would see new entries in package.json
"axios": "^0.18.0",
"formik": "^1.5.1",
"react-router-dom": "^5.0.0",
You can run ‘npm start’ to relaunch the front end app loading up all the new frameworks.
Creating a List Courses Component
Let’s create a new component for showing the List of courses - ListCoursesComponent.jsx. For now, let’s hardcode a course into the course list.
/src/component/ListCoursesComponent.jsx
class ListCoursesComponent extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<h3>All Courses</h3>
<div className="container">
<table className="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Id</th>
<th>Description</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>Learn Full stack with Spring Boot and Angular</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default ListCoursesComponent
Things to Note:
- It’s a simple component. Returning a hardcoded table displaying a list of courses.
Let’s update the InstructorApp component to display the ListCoursesComponent.
/src/component/InstructorApp.jsx
class InstructorApp extends Component {
render() {
return (<>
<h1>Instructor Application</h1>
<ListCoursesComponent/>
</>
)
}
}
export default InstructorApp
We are importing the ListCoursesComponent and displaying it in the InstructorApp.
When you launch the React app in the browser, it will appear as shown below:
Invoking Retrieve Courses REST API from React Component
We had created the REST API for retrieving the list of courses earlier. To call the REST API we would need to use a framework called axios.
Axios is a Promise based HTTP client for the browser and node.js
Axios is a frontend framework that helps you make
- REST API calls with different request methods including GET, POST, PUT, DELETE etc
- Intercept Front end REST API calls and add headers and request content
Let’s create a data service method to call the REST API.
/src/service/CourseDataService.js
import axios from 'axios'
const INSTRUCTOR = 'in28minutes'
const COURSE_API_URL = 'http://localhost:8080'
const INSTRUCTOR_API_URL = `${COURSE_API_URL}/instructors/${INSTRUCTOR}`
class CourseDataService {
retrieveAllCourses(name) {
return axios.get(`${INSTRUCTOR_API_URL}/courses`);
}
}
export default new CourseDataService()
Important points to note:
const INSTRUCTOR_API_URL = `${COURSE_API_URL}/instructors/${INSTRUCTOR}`- We are forming the URL to call in a reusable way.axios.get(`${INSTRUCTOR_API_URL}/courses`)- Call the REST API with the GET method.export default new CourseDataService()- We are creating an instance of CourseDataService and making it available for other components.
To make the REST API call, we would need to call the CourseDataService - retrieveAllCourses method from the ListCoursesComponent
Important snippets are shown below:
class ListCoursesComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.refreshCourses = this.refreshCourses.bind(this)
}
componentDidMount() {
this.refreshCourses();
}
refreshCourses() {
CourseDataService.retrieveAllCourses(INSTRUCTOR)//HARDCODED
.then(
response => {
console.log(response);
}
)
}
....
}
Things to note:
componentDidMount()- React defines a component lifecycle. componentDidMount will be called as soon as the component is mounted. We are calling refreshCourses as soon as a component is mounted.this.refreshCourses = this.refreshCourses.bind(this)- Any method in a react component should be bound to this. -CourseDataService.retrieveAllCourses(INSTRUCTOR).then- This would make the call to the REST API. You can define how to process the response in the then method.
When you run the react app in the browser right now, you would see the following errors in the console
[Error] Origin http://localhost:3000 is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Origin.
[Error] XMLHttpRequest cannot load http://localhost:8080/instructors/in28minutes/courses due to access control checks.
[Error] Failed to load resource: Origin http://localhost:3000 is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Origin. (courses, line 0)
[Error] Unhandled Promise Rejection: Error: Network Error
(anonymous function) (0.chunk.js:1097)
promiseReactionJob
The Backend Spring Boot REST API is running on http://localhost:8080, and it is not allowing requests from other servers - http://localhost:3000, in this example.
Let’s configure Rest Resource to allow access from specific servers.
@CrossOrigin(origins = { "http://localhost:3000", "http://localhost:4200" })
@RestController
public class CourseResource {
An important thing to note
- @CrossOrigin(origins = { “http://localhost:3000”, “http://localhost:4200” }) - Allow requests from specific origins
- We will use 3000 to run React and Vue JS apps, and we use 4200 to run Angular apps. Hence we are allowing requests from both ports.
If you refresh the page again, you would see the response from server printed in the console.
We would need to use the data from the response and show it on the component.
In React, we use the state to do that.
Following snippet highlights the significant changes
class ListCoursesComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
courses: [],
message: null
}
this.refreshCourses = this.refreshCourses.bind(this)
}
componentDidMount() {
this.refreshCourses();
}
refreshCourses() {
CourseDataService.retrieveAllCourses(INSTRUCTOR)//HARDCODED
.then(
response => {
console.log(response);
this.setState({ courses: response.data })
}
)
}
....
}
Important things to note:
this.state = {courses: [],message: null}- To display courses, we need to make them available to the component. We add courses to the state of the component and initialize it in the constructor.response => {this.setState({ courses: response.data })}- When the response comes back with data, we update the state.
We have data in the state. How do we display it?
We need to update the render method.
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<h3>All Courses</h3>
<div className="container">
<table className="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Id</th>
<th>Description</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{
this.state.courses.map(
course =>
<tr key={course.id}>
<td>{course.id}</td>
<td>{course.description}</td>
</tr>
)
}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
)
}
Important things to note
this.state.courses.map(- Allow you to loop around a list of items and define how each item should be displayed.key={course.id}- A key is used to uniquely identify a row.{course.id}- In JSX, we use {} to execute JavaScript code.
When you launch the React app in the browser, it will appear as shown below:
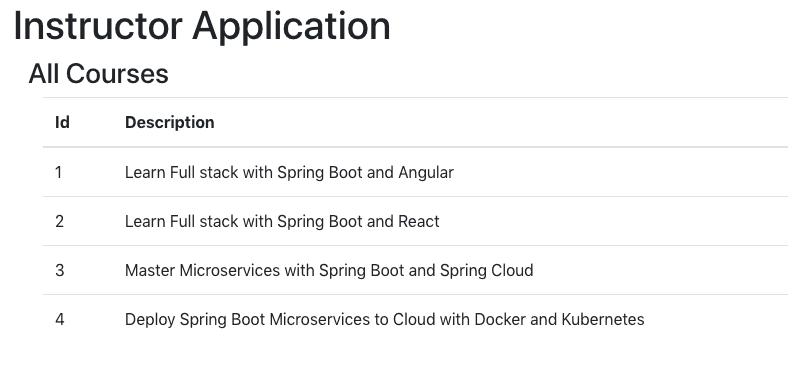
Congratulations! You have successfully integrated React with a REST API. Time to celebrate!
Step 4: Adding Delete Feature to List Courses Page
To be able to do this
- We need a REST API in Spring Boot Backend for deleting a course
- We would need to update React frontend to use the API
Adding Delete Method in the Backend REST API
It should be easy.
Snippets below show how we create a simple deleteById method in CoursesHardcodedService and expose it from CourseResource.
@Service
public class CoursesHardcodedService {
public Course deleteById(long id) {
Course course = findById(id);
if (course == null)
return null;
if (courses.remove(course)) {
return course;
}
return null;
}
public class CourseResource {
@DeleteMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteCourse(@PathVariable String username, @PathVariable long id) {
Course course = courseManagementService.deleteById(id);
if (course != null) {
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
Important things to note:
@DeleteMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses/{id}")- We are mapping the Delete Request Method with two path variables@PathVariable String username, @PathVariable long id- Defining the variables for Path VariablesResponseEntity.noContent().build()- If Request is successful, return no content backResponseEntity.notFound().build()- If delete failed, return error - resource not found.
Enhancing React app with Delete Course Feature
Let’s add deleteCourse method to CourseDataService. As you can see it execute the delete request to specific course api url.
deleteCourse(name, id) {
//console.log('executed service')
return axios.delete(`${INSTRUCTOR_API_URL}/courses/${id}`);
}
We can add a delete button corresponding to each of the courses:
<td><button className="btn btn-warning" onClick={() => this.deleteCourseClicked(course.id)}>Delete</button></td>
On click of the button we are calling the deleteCourseClicked method passing the course id. The implementation for deleteCourseClicked is shown below:
When we get a successful response for delete API call, we set a message into state and refresh the courses list.
deleteCourseClicked(id) {
CourseDataService.deleteCourse(INSTRUCTOR, id)
.then(
response => {
this.setState({ message: `Delete of course ${id} Successful` })
this.refreshCourses()
}
)
}
We display the message just below the header
<h3>All Courses</h3>
{this.state.message && <div class="alert alert-success">{this.state.message}</div>}
Of course - we have to ensure that the method is bound to this in the constructor.
this.deleteCourseClicked = this.deleteCourseClicked.bind(this)
Complete ListCoursesComponent, at this stage, is shown below:
class ListCoursesComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
courses: [],
message: null
}
}
render() {
console.log('render')
return (
<div className="container">
<h3>All Courses</h3>
{this.state.message && <div class="alert alert-success">{this.state.message}</div>}
<div className="container">
<table className="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Id</th>
<th>Description</th>
<th>Delete</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{
this.state.courses.map(
course =>
<tr key={course.id}>
<td>{course.id}</td>
<td>{course.description}</td>
<td><button className="btn btn-warning" onClick={() => this.deleteCourseClicked(course.id)}>Delete</button></td>
</tr>
)
}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
)
}
When you launch the React app in the browser, it will appear as shown below:
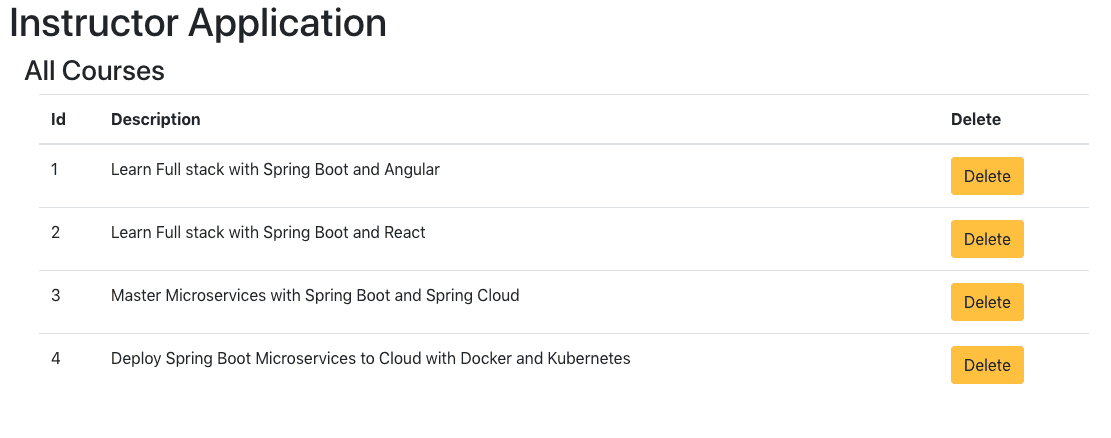
When you click the delete button, the course will be deleted.
Updating Course Details
To be able to update the course details, we would need to create a new component to represent the todo form.
Let’s start with creating a simple component.
/src/component/CourseComponent.jsx
class CourseComponent extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h1>Course Details</h1>
)
}
}
export default CourseComponent
Implementing Routing
When the user clicks the update course button on the course listing page, we would want to route to the course page. How do we do it? That’s where Routing comes into the picture.
/src/component/InstructorApp.jsx
class InstructorApp extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<>
<h1>Instructor Application</h1>
<Switch>
<Route path="/" exact component={ListCoursesComponent} />
<Route path="/courses" exact component={ListCoursesComponent} />
<Route path="/courses/:id" component={CourseComponent} />
</Switch>
</>
</Router>
)
}
}
export default InstructorApp
We are defining a Router around all the components and configuring paths to each of them.
http://localhost:3000/takes you to home pagehttp://localhost:3000/coursestakes you to course listing pagehttp://localhost:3000/courses/2takes you to course page
When you launch the React app in the browser using this URL http://localhost:3000/courses/2, it will appear as shown below:
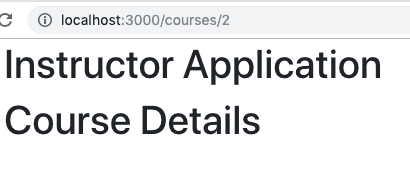
Adding Update Button to Course Listing Page
Let’s add update button to the course listing page.
/src/component/ListCoursesComponent.jsx
.....
<th>Update</th>
....
<td><button className="btn btn-success" onClick={() => this.updateCourseClicked(course.id)}>Update</button></td>
We can create the add updateCourseClicked method to redirect to Course Component and add the binding in the constructor method.
...
this.updateCourseClicked = this.updateCourseClicked.bind(this)
...
updateCourseClicked(id) {
console.log('update ' + id)
this.props.history.push(`/courses/${id}`)
}
Adding Add button to Course Listing Page
Let’s add an Add button at the bottom of Course Listing Page.
/src/component/ListCoursesComponent.jsx
<div className="row">
<button className="btn btn-success" onClick={this.addCourseClicked}>Add</button>
</div>
Let’s add the appropriate binding and the method to handle click of Add button.
//In constructor
this.addCourseClicked = this.addCourseClicked.bind(this)
addCourseClicked() {
this.props.history.push(`/courses/-1`)
}
When you launch the React app in the browser using this URL http://localhost:3000, it will appear as shown below:

Clicking any of the Update or Add buttons would take you to the Course Component.
Create API to Retrieve Specific Course Details
Now that we have the course component beinging rendered on the click of update button, let’s start focusing on getting the course details from the REST API.
Let’s add findById method to CoursesHardcodedService. It retrieves the details of a specific course based on it.
public Course findById(long id) {
for (Course course: courses) {
if (course.getId() == id) {
return course;
}
}
return null;
}
Let’s add getCourse method to CourseResource class. It exposes the GET method to get the details of a specific course based on id.
@GetMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses/{id}")
public Course getCourse(@PathVariable String username, @PathVariable long id) {
return courseManagementService.findById(id);
}
Invoking the API from Course Component
How do we invoke the retrieve course details from the React frontend?
Let’s add retrieveCourse method to CourseDataService
retrieveCourse(name, id) {
return axios.get(`${INSTRUCTOR_API_URL}/courses/${id}`);
}
We would want to call the retrieveCourse method in CourseDataService on the load of CourseComponent.
How do we do it?
Yes. componentDidMount is the right solution.
Before we get to it we would need to be able to get the course id from the URL. In the course details page, we are redirecting to the url /courses/${id}. From the path parameter, we would want to capture the id. We can use this.props.match.params.id to get the id from path parameters.
The code listing below shows the updated CourseComponent.
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { Formik, Form, Field, ErrorMessage } from 'formik';
import CourseDataService from '../service/CourseDataService';
const INSTRUCTOR = 'in28minutes'
class CourseComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
id: this.props.match.params.id,
description: ''
}
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log(this.state.id)
// eslint-disable-next-line
if (this.state.id == -1) {
return
}
CourseDataService.retrieveCourse(INSTRUCTOR, this.state.id)
.then(response => this.setState({
description: response.data.description
}))
}
render() {
let { description, id } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h3>Course</h3>
<div>{id}</div>
<div>{description}</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default CourseComponent
We are setting the details of the course into state.
We are initializing state in the constructor.
this.state = {
id: this.props.match.params.id,
description: ''
}
In componentDidMount, we are calling the CourseDataService.retrieveCourse to get the details for a course. Once we have the details, we are updating the state.
CourseDataService.retrieveCourse(INSTRUCTOR, this.state.id)
.then(response => this.setState({
description: response.data.description
}))
We are updating the render method to show the course details from component state.
render() {
let { description, id } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h3>Course</h3>
<div>{id}</div>
<div>{description}</div>
</div>
)
}
let { description, id } = this.state is called destructing. This is similar to writing code shown below.
let description = this.state.description
let id = this.state.id
When you try to update a course, you would see the screen below.

When you try to create a course, you would see the screen below.

This is because of the logic in componentDidMount to not invoke the course API for a new todo.
if (this.state.id == -1) {
return
}
Create a Form using Formik
Now that we have loaded up the details of a specific course, let’s shift out our attention to editing them and saving them back to the database.
To edit course details, we need a form. The most popular form framework with React is formik. We already added formik to our package.json using the command npm add formik.
Let’s now create a simple form using formik.
render() {
let { description, id } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h3>Course</h3>
<div className="container">
<Formik
initialValues={{ id, description }}
>
{
(props) => (
<Form>
<fieldset className="form-group">
<label>Id</label>
<Field className="form-control" type="text" name="id" disabled />
</fieldset>
<fieldset className="form-group">
<label>Description</label>
<Field className="form-control" type="text" name="description" />
</fieldset>
<button className="btn btn-success" type="submit">Save</button>
</Form>
)
}
</Formik>
</div>
</div>
)
}
Following are some of the important details:
let { description, id } = this.state- Creating local variable using destructuring<Formik initialValues={{ id, description }}>- Initialing Formik with the values loaded from state<Field className="form-control" type="text" name="id" disabled />- Creating a disabled text element for id. The name of element should match the name in state.<Field className="form-control" type="text" name="description" />- Creating a text element for description. The name of element should match the name in state.<button className="btn btn-success" type="submit">Save</button>- Adding a submit button.
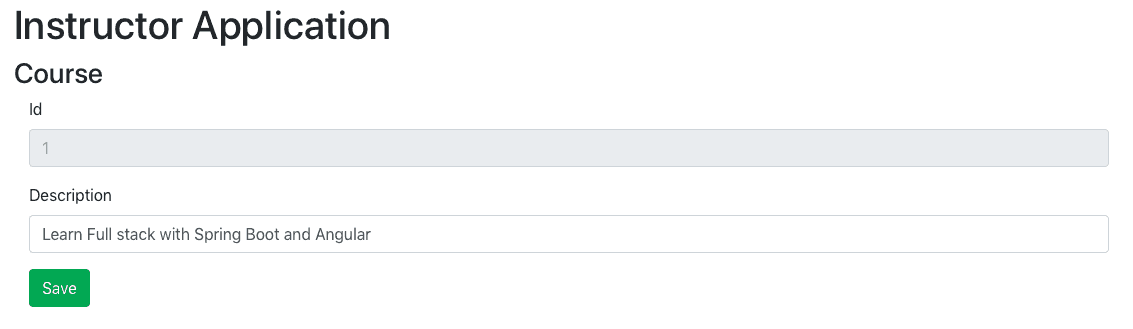
When you try to update a course, you would see the screen below.
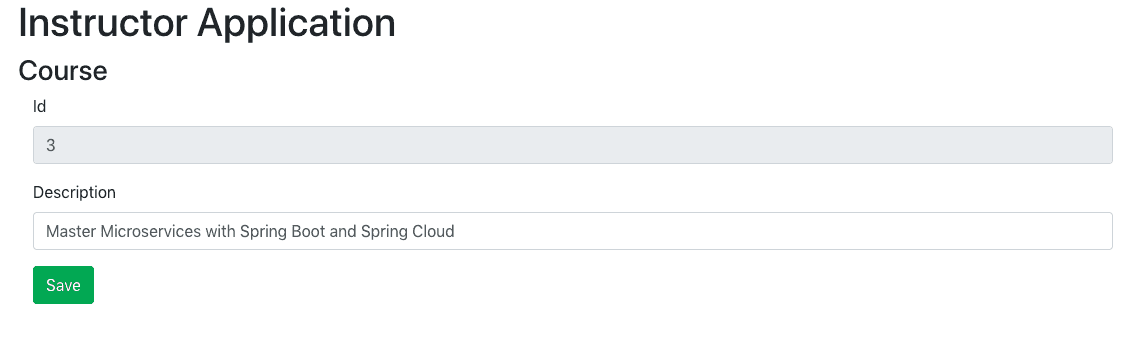
Adding Handling of Submit Event
Let’s try to handle the Submit event now.
Let’s create an onSubmit method to log the values
onSubmit(values) {
console.log(values);
}
Let’s bind the onSubmit method to this in the constructor.
this.onSubmit = this.onSubmit.bind(this)
It’s time to tie up the form with the onSubmit method. The key snippet is onSubmit={this.onSubmit}.
<Formik
initialValues={{ id, description }}
onSubmit={this.onSubmit}
>
When you click Submit, the form details are now printed to the console.
{id: "2", description: "Learn Microservices"}
Adding Validation using Formik
What’s a form without validation?
Let’s add a validate method.
validate(values) {
let errors = {}
if (!values.description) {
errors.description = 'Enter a Description'
} else if (values.description.length < 5) {
errors.description = 'Enter atleast 5 Characters in Description'
}
return errors
}
We are adding two validations:
- check for empty description
- check for a minimum length of 5
You can add other validations as you need.
As usual, let’s bind it to this in the constructor.
this.validate = this.validate.bind(this)
Let’s ties this up with the form. The key snippet is validate={this.validate}. We do not want to validate on change of value or on blur of the field. Let’s keep things simple. enableReinitialize={true} is needed to ensure that we can reload the form for existing todo.
<Formik
initialValues={{ id, description }}
onSubmit={this.onSubmit}
validateOnChange={false}
validateOnBlur={false}
validate={this.validate}
enableReinitialize={true}>
If you run the page right now and submit invalid description, you would see that validations prevent the form from getting submitted.
How do we see validation messages on the screen?
Formik provides ErrorMessage.
Let’s add error message to the field:
<ErrorMessage name="description" component="div"
className="alert alert-warning" />
When you try to update a course, you would see the screen below.
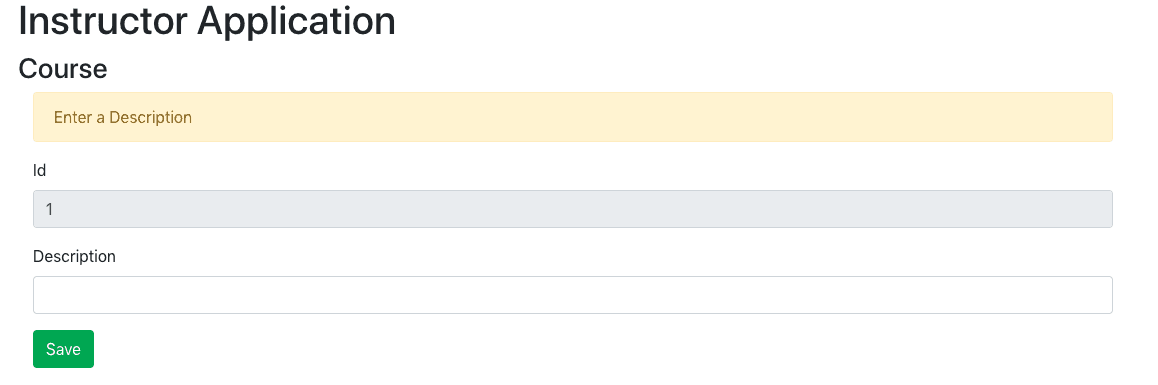
Updating Course Details on click of submit
Now that the form is ready, we would want to call the backend API to save the course details.
Let’s quickly create the API to Update and Create Courses.
Create API to Update Course
Let’s add a save method to CoursesHardcodedService to handle creation and updation of course.
public Course save(Course course) {
if (course.getId() == -1 || course.getId() == 0) {
course.setId(++idCounter);
courses.add(course);
} else {
deleteById(course.getId());
courses.add(course);
}
return course;
}
Let’s add a method to the Resource class to update the course. We are using PUT method to update the course. On course updation, we are returning 200 status with updaated course details in the body.
@PutMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Course> updateCourse(@PathVariable String username, @PathVariable long id,
@RequestBody Course course) {
Course courseUpdated = courseManagementService.save(course);
return new ResponseEntity<Course>(courseUpdated, HttpStatus.OK);
}
Adding API to Create Course
Let’s add a method to the Resource class to create the course. We are using POST method to create the course. On course updation, we are returning a status of CREATED.
@PostMapping("/instructors/{username}/courses")
public ResponseEntity<Void> createCourse(@PathVariable String username, @RequestBody Course course) {
Course createdCourse = courseManagementService.save(course);
// Location
// Get current resource url
/// {id}
URI uri = ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentRequest().path("/{id}").buildAndExpand(createdCourse.getId())
.toUri();
return ResponseEntity.created(uri).build();
}
Invoking Update and Create APIs from Course Screen
Now that the REST API is ready, let’s create the frontend methods to call them.
Let’s create respective methods in the CourseDataService. updateCourse uses a put and createCourse uses post.
class CourseDataService {
updateCourse(name, id, course) {
return axios.put(`${INSTRUCTOR_API_URL}/courses/${id}`, course);
}
createCourse(name, course) {
return axios.post(`${INSTRUCTOR_API_URL}/courses/`, course);
}
Let’s update the CourseComponent to invoke the right service on the click of the submit button.
onSubmit(values) {
let username = INSTRUCTOR
let course = {
id: this.state.id,
description: values.description,
targetDate: values.targetDate
}
if (this.state.id === -1) {
CourseDataService.createCourse(username, course)
.then(() => this.props.history.push('/courses'))
} else {
CourseDataService.updateCourse(username, this.state.id, course)
.then(() => this.props.history.push('/courses'))
}
console.log(values);
}
We are creating a course object with the updated details and calling the appropriate method on the CourseDataService. Once the request is successful, we are redirecting the user to the course listing page using this.props.history.push('/courses').
Downloading the Complete Maven Project With Code Examples
Following GitHub repository hosts the complete frontend and backend projects - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-react-fullstack-examples/tree/master/spring-boot-react-crud-full-stack-with-maven
Our Github repository has all the code examples - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-react-examples/