This guide will help you understand how Spring Boot Starter Projects enable the key goal of Spring Boot - Quick Start to developing production ready applications.

You will learn
- What features are provided by Spring Boot Starter Projects?
- We will look at an example of Starter Projects
- We will look at Spring Boot Starter Web
- Get an overview of different starter projects provided by Spring Boot.
Tools you will need
- Maven 3.0+ is your build tool
- Your favorite IDE. We use Eclipse.
- JDK 17
Why do we need Spring Boot Starter Projects?
Consider an example project that does not use a starter to better grasp what starting projects provide.
What if we do not have starter projects?
Assume we wish to create a web application using Spring MVC.
First and foremost, we must decide which frameworks to utilise, which versions of frameworks to employ, and how to link them.
Some of the dependencies we utilise in our Spring MVC Course are listed below. Spring MVC, Jackson Databind (for data binding), Hibernate-Validator (for server side validation using Java Validation API), and Log4j are among them (for logging). We had to select compatible versions of all of these frameworks when developing this course.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.14.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>8.0.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-bom</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
To get everything hooked together, we had to add settings. Settings for the dispatcher servlet, view resolver, error page, and web jars, among other things.
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/views/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="classpath:messages" />
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
</bean>
<mvc:resources mapping="/webjars/**" location="/webjars/" />
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/todo-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
We would need to do similar things while utilising JPA. We must provide the jars as well as the settings for the datasource, entity manager, transaction manager, and so on.
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClass" value="${db.driver}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${db.url}" />
<property name="user" value="${db.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${db.password}" />
</bean>
<jdbc:initialize-database data-source="dataSource">
<jdbc:script location="classpath:config/schema.sql" />
<jdbc:script location="classpath:config/data.sql" />
</jdbc:initialize-database>
<bean
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean"
id="entityManagerFactory">
<property name="persistenceUnitName" value="hsql_pu" />
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory" />
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
Spring Boot Starter Projects
Here’s what the Spring Boot documentations says about starters.
Starters are a set of convenient dependency descriptors that you can include in your application. You get a one-stop-shop for all the Spring and related technology that you need, without having to hunt through sample code and copy paste loads of dependency descriptors. For example, if you want to get started using Spring and JPA for database access, just include the spring-boot-starter-data-jpa dependency in your project, and you are good to go.
Let’s consider an example starter - Spring Boot Starter Web.
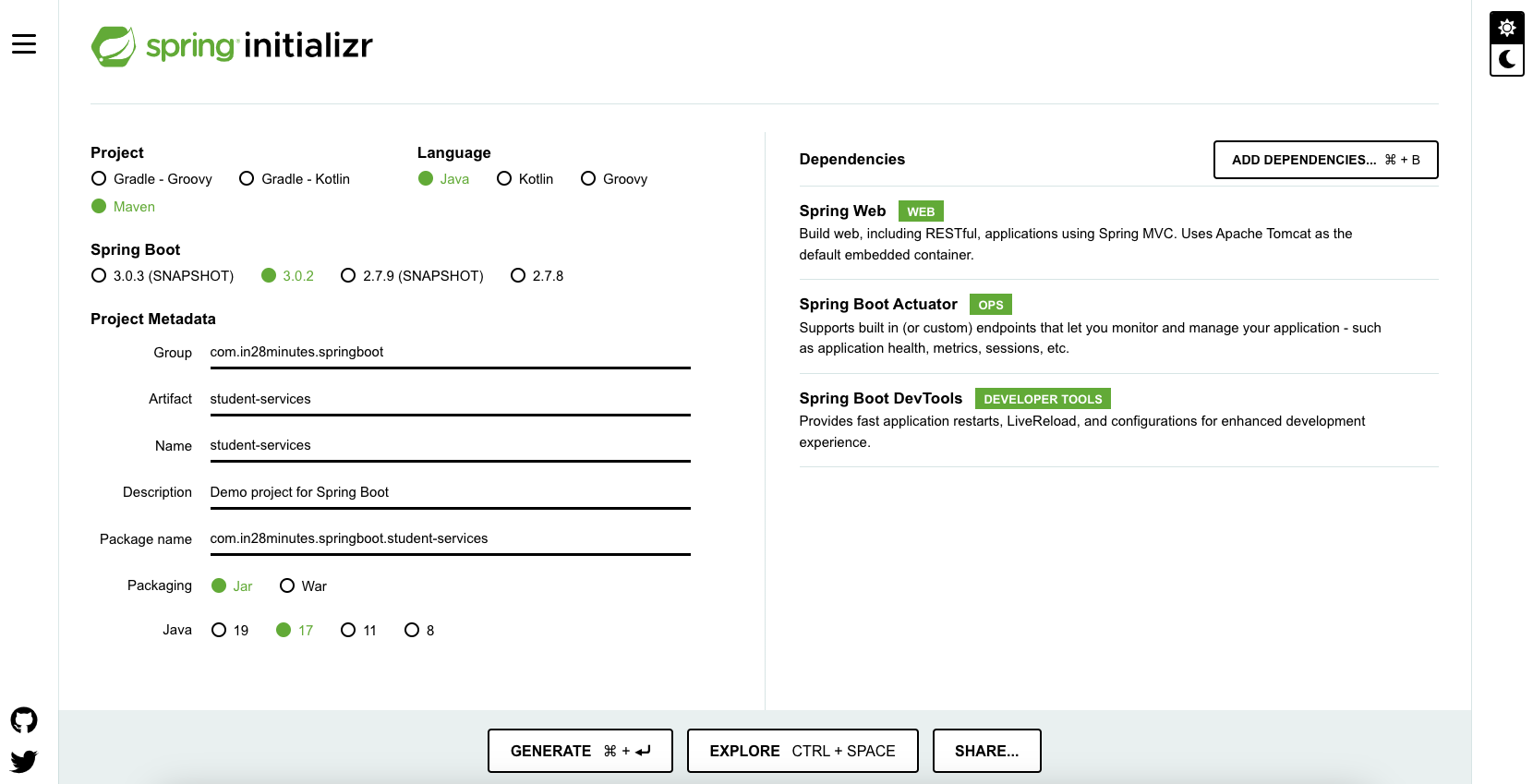
If you want to develop a web application or an application to expose restful services, Spring Boot Start Web is the starter to pick. Lets create a quick project with Spring Boot Starter Web using Spring Initializr.
Creating REST Services Application with Spring Initializr
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ is great tool to bootstrap your Spring Boot projects.

As shown in the image above, following steps have to be done.
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following
- Choose
com.in28minutes.springbootas Group - Choose
student-servicesas Artifact - Choose following dependencies
- Web
- Actuator
- DevTools
- Choose
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the project into Eclipse.
- If you want to understand all the files that are part of this project, you can go here.
Spring Boot Starter Web
Spring Boot Starter Web has two crucial features.
- Compatible Dependencies that are needed to develop web applications
- Auto Configuration
Dependency for Spring Boot Starter Web
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
Dependencies
Following screenshot shows the different dependencies that are added in to our application

Dependencies can be classified into:
- Spring - core, beans, context, aop
- Web MVC - (Spring MVC)
- Jackson - for JSON Binding
- Validation - Hibernate Validator, Validation API
- Embedded Servlet Container - Tomcat
- Logging - logback, slf4j
All of these requirements would be used by any regular web application. Spring Boot Starter Site already has them. As a developer, I would not have to be concerned about their dependencies or their compatible version
Auto Configuration
Spring Boot Starter Web automatically configures the essentials. To explore the functionality added by Spring Boot Starter Web, run StudentServicesApplication.java as a Java Application and examine the log.
Mapping servlet: 'dispatcherServlet' to [/]
Mapped "{[/error]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<java.util.Map<java.lang.String, java.lang.Object>> org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.BasicErrorController.error(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest)
Mapped URL path [/webjars/**] onto handler of type [class org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler]
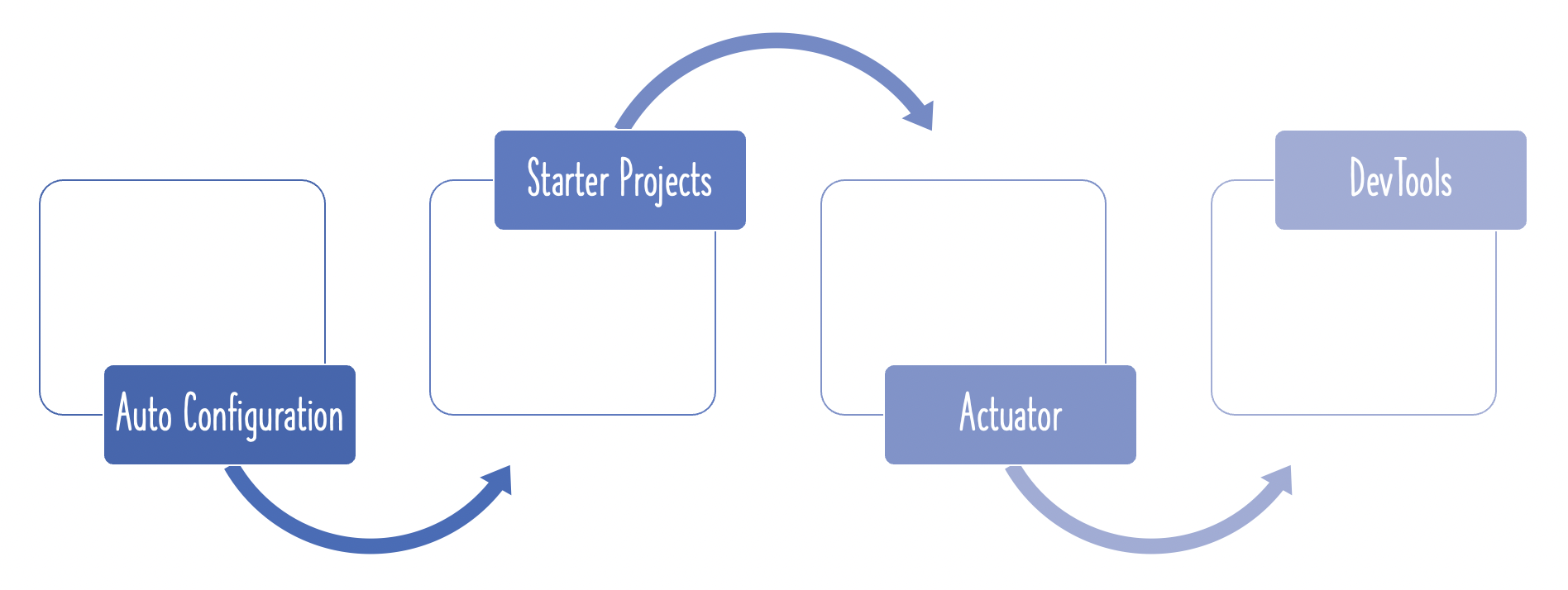
Spring Boot Starter Web auto-configures
- Dispatcher Servlet
- Error Page
- Web Jars to manage your static dependencies
- Embedded Servlet Container - Tomcat is the default
The image below shows the different things that might be auto configured by Spring Boot Starter Web

Spring Boot Starter Project Options
As we can see from Spring Boot Starter Web, starting projects allow us to get started fast with designing various sorts of apps.
- spring-boot-starter-web-services - SOAP Web Services
- spring-boot-starter-web - Web & RESTful applications
- spring-boot-starter-test - Unit testing and Integration Testing
- spring-boot-starter-jdbc - Traditional JDBC
- spring-boot-starter-hateoas - Add HATEOAS features to your services
- spring-boot-starter-security - Authentication and Authorization using Spring Security
- spring-boot-starter-data-jpa - Spring Data JPA with Hibernate
- spring-boot-starter-cache - Enabling Spring Framework’s caching support
- spring-boot-starter-data-rest - Expose Simple REST Services using Spring Data REST
There are a few starters for technical stuff as well
- spring-boot-starter-actuator - To use advanced features like monitoring & tracing to your application out of the box
- spring-boot-starter-undertow, spring-boot-starter-jetty, spring-boot-starter-tomcat - To pick your specific choice of Embedded Servlet Container
- spring-boot-starter-logging - For Logging using logback
- spring-boot-starter-log4j2 - Logging using Log4j2