Spring Boot Goals:
- Allows for the rapid development of production-ready apps.
- It provides common non-functional features.
- Embedded servers
- Metrics
- Health checks
- Externalized configuration
What Spring Boot is NOT!
- ZERO code generation.
- There is no application server or web server.
Features
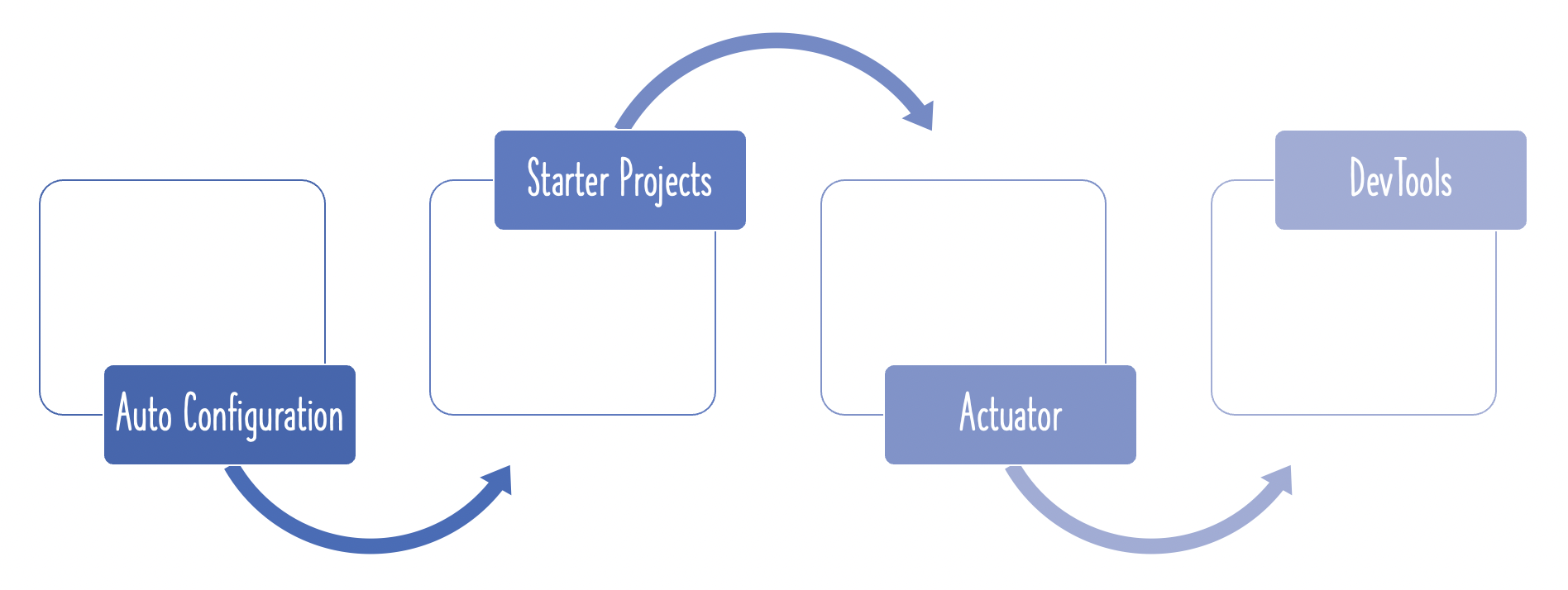
- Quick Starter Projects with Auto Configuration
- Web
- JPA
- Embedded Servers
- Tomcat, Jetty or Undertow
- Production-ready features
- Metrics and health checks
- Externalized configuration
URLs
- http://localhost:8080/books => Few hardcoded books
Step by Step Details
- Step 1 : Introduction to Spring Boot—Goals and Important Features
- Step 2: Create Spring Applications Prior to Spring Boot
- Step 3: Creating a Spring Boot Application with Spring Initializr
- Step 4 : Creating a Simple REST Controller
- Step 5 : What is Spring Boot Auto Configuration?
- Recommended Reading-http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-auto-configuration
- Spring-based apps may be highly customised. Spring MVC requires us to configure component scan, dispatcher servlet, view resolver, and web jars (for serving static content), among other things. We would need to configure a datasource, an entity management factory, and a transaction manager, among other things, when using Hibernate/JPA. The Spring Boot introduces a different way of thinking about this: Can we incorporate more intelligence into this? Can we automatically setup certain beans when a spring mvc jar is introduced to an application?
- Step 6 : Spring Boot vs. Spring vs. Spring MVC
- Recommended Reading-http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-vs-spring-mvc-vs-spring
- Spring is about
Dependency Injection. It makes it easy to develop loosely coupled applications. It makes applications testable. - Spring MVC brings loose coupling to web MVC application development with features like
Dispatcher Servlet, View Resolver, etc. - Spring Boot eliminates the need for manual configuration with Spring and Spring MVC. You can use Spring and Spring MVC without needing a lot of configuration.
- Spring Boot aims to enable production-ready applications in quick time.
- Actuator : Enables Advanced
Monitoring and Tracingof applications. - Embedded Server Integrations : Because the server is built into the application, I don’t need to install a separate application server on the server.
- Default Error Handling
- Actuator : Enables Advanced
- Step 7 : Spring Boot Starter Projects: Starter Web and Starter JPA
- Recommended Reading-http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-starter-projects
Startersare a set of convenientdependency descriptorsthat you can include in your application. You get a one-stop-shop for all the Spring and related technology that you need, without having to hunt through sample code and copy-paste loads of dependency descriptors. For example, if you want to get started using Spring and JPA for database access, just include thespring-boot-starter-data-jpadependency in your project, and you are good to go.
- Step 8: A Summary of the Different Spring Boot Starter Projects
- As we see from Spring Boot Starter Web, starter projects help us to quickly get started with developing specific types of applications.
spring-boot-starter-web-services-SOAP Web Servicesspring-boot-starter-web-Web & RESTful applicationsspring-boot-starter-test-Unit Testing and Integration Testingspring-boot-starter-jdbc-Traditional JDBCspring-boot-starter-hateoas-Add HATEOAS features to your services.spring-boot-starter-security-Authentication and Authorization using Spring Securityspring-boot-starter-data-jpa-Spring Data JPA with Hibernatespring-boot-starter-cache-Enabling Spring Framework’s caching supportspring-boot-starter-data-rest-Expose Simple REST Services using Spring Data RESTspring-boot-starter-actuator-To add advanced features such as monitoring and tracing to your application right away.spring-boot-starter-undertow, spring-boot-starter-jetty, spring-boot-starter-tomcat-To pick your specific choice of Embedded Servlet Containerspring-boot-starter-logging-For Logging using Logbackspring-boot-starter-log4j2-Logging using Log4j2
- Step 9 : Spring Boot Actuator
- The Spring Boot starter actuator actually exposes a lot of REST services, and these services are compliant with the standard called the HAL standard. And we would use a hal explorer so that we can browse through the data which is provided by these services. The Spring Boot Actuator exposes a lot of data-application info:
metrics, dump, beans, env, config properties, audit events, heap dump, loggers, trace, health mappings, and auto config. The Actuator provides more metadata about your application.
- The Spring Boot starter actuator actually exposes a lot of REST services, and these services are compliant with the standard called the HAL standard. And we would use a hal explorer so that we can browse through the data which is provided by these services. The Spring Boot Actuator exposes a lot of data-application info:
- Step 10 : Spring Boot Developer Tools
- Why do you need to restart your server for every Java and JSP change?
- The Spring Boot Developer Tools enable dynamic reloading of modified changes.
- Spring Boot - Conclusion
Complete Code Example
/pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.in28minutes.springboot.basics</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-in-10-steps</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>springboot-in-10-steps</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-rest-hal-explorer</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</project>
/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/basics/springbootin10steps/Book.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps;
public record Book(long id, String name, String author) {
public static String UNKNOWN_AUTHOR = "Unknown";
public static String UNNAMED = "Unnamed";
public Book {
Objects.requireNonNull(name);
Objects.requireNonNull(author);
}
public Book(String name) {
this(name, UNKNOWN_AUTHOR);
}
public static Book unnamed(String author) {
return new Book(UNNAMED, author);
}
}
/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/basics/springbootin10steps/BooksController.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class BooksController {
@GetMapping("/books")
public List<Book> getAllBooks() {
return List.of(new Book(1L, "Mastering Spring 5.2", "Ranga Karanam"));
}
}
/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/basics/springbootin10steps/SpringbootIn10StepsApplication.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootIn10StepsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var applicationContext =
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootIn10StepsApplication.class, args);
applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()
.forEach(System.out::println)
}
}
/src/main/resources/application.properties
#logging.level.org.springframework = DEBUG
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
/src/test/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/basics/springbootin10steps/SpringbootIn10StepsApplicationTests.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootIn10StepsApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
}
}