This post will show you how to offer RESTful APIs with Spring Boot, JPA/Hibernate, Spring Data, and Spring Data REST. H2 will be used as the in-memory database.
You will learn
- How do you make a Spring Boot project with Spring Boot Starter JPA, Spring Boot Data Rest Starter, and H2?
- How to expose RESTful API using Spring Boot Data Rest?
- How to connect a Spring Boot project to database using JPA/Hibernate?
- How to create a simple JPA Entity with a primary key?
- How to write a simple repository interface extending JpaRepository interface?
Structure of the Project Code
The screenshot below depicts the framework of the project we will be creating.
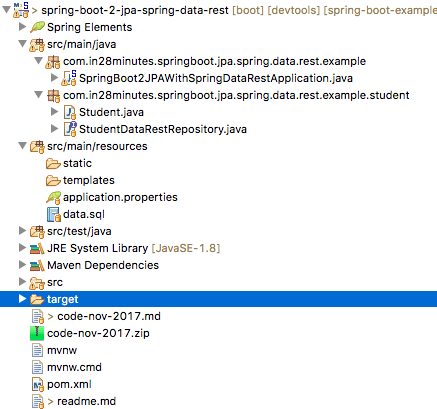
A few details:
Student.java- Entity bean to store student details.StudentDataRestRepository.java- Extends PagingAndSortingRepository. Acts as a @RepositoryRestResource to provide RESTful API/Services to update/retrieve Student entities.data.sql- To supply the initial student data, we utilisedata.sql.- SpringBoot2JPAWithSpringDataRestApplication.java - The primary Spring Boot Application class used to start the application.
pom.xml- This package contains all of the dependencies required to develop this project. In addition to Developer Tools and H2, we will utilise Spring Boot Starter JPA, Spring Boot Data REST Starter, and Spring Boot Starter Web.
You will require the following tools:
- Maven 3.0+ is your build tool
- Your favorite IDE. We use Eclipse or IntelliJ.
- JDK 17
Maven Project Completion using Code Samples
Our Github repository has all the code examples - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-examples/tree/master/spring-boot-2-jpa-spring-data-rest
How Does Spring Data REST Work in the Big Picture?
Let’s start with JPA and work our way up to Spring Data and Spring Data REST.
JPA
JPA allows you to map application classes to database tables.
- Entity Manager - Entity manager may manage your entities after the mappings are defined. Entity Manager manages all database interactions.
- Java Persistence Query Language (JPQL) - Offers methods for writing queries to do entity searches. It is critical to recognise that these are not SQL queries. JPQL queries are already aware of the mappings that exist between entities. More criteria can be added as needed.
- Criteria API specifies a Java-based API for doing database searches.
What is Spring Data?
From http://projects.spring.io/spring-data/
The objective of Spring Data is to provide a familiar and consistent Spring-based programming model for data access while keeping the unique characteristics of the underlying data store. It makes data access technologies, relational and non-relational databases, map-reduce frameworks, and cloud-based data services simple to utilise.
To make things easier, Spring Data provides Abstractions (interfaces) that may be used regardless of the underlying data source.
An example is shown below
interface TodoRepository extends CrudRepository<Todo, Long> {
Core idea is that
Without writing a lot of code, you may establish a basic repository and use it to insert, update, remove, and retrieve todo entities from the database.
Spring Data REST
Spring Data REST may be used to deliver HATEOAS RESTful resources that are nested within Spring Data repositories.
An example using JPA is shown below
@RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel = "todos", path = "todos")
public interface TodoRepository
extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Todo, Long> {
Without writing a lot of code, we can expose RESTful API around Spring Data Repositories.
A few example REST Services that are automatically exposed are shown below:
POST
- URL : http://localhost:8080/todos
- Use Header : Content-Type:application/json
Request Content
{
"user": "Jill",
"desc": "Learn Hibernate",
"done": false
}
Response Content
{
"user": "Jill",
"desc": "Learn Hibernate",
"done": false,
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
},
"todo": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
}
}
}
The response contains the href of the newly created resource.
GET
- URI - http://localhost:8080/todos
Response
{
"_embedded" : {
"todos" : [ {
"user" : "Jill",
"desc" : "Learn Hibernate",
"done" : false,
"_links" : {
"self" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
},
"todo" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
}
}
} ]
},
"_links" : {
"self" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos"
},
"profile" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/profile/todos"
},
"search" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/search"
}
},
"page" : {
"size" : 20,
"totalElements" : 1,
"totalPages" : 1,
"number" : 0
}
}
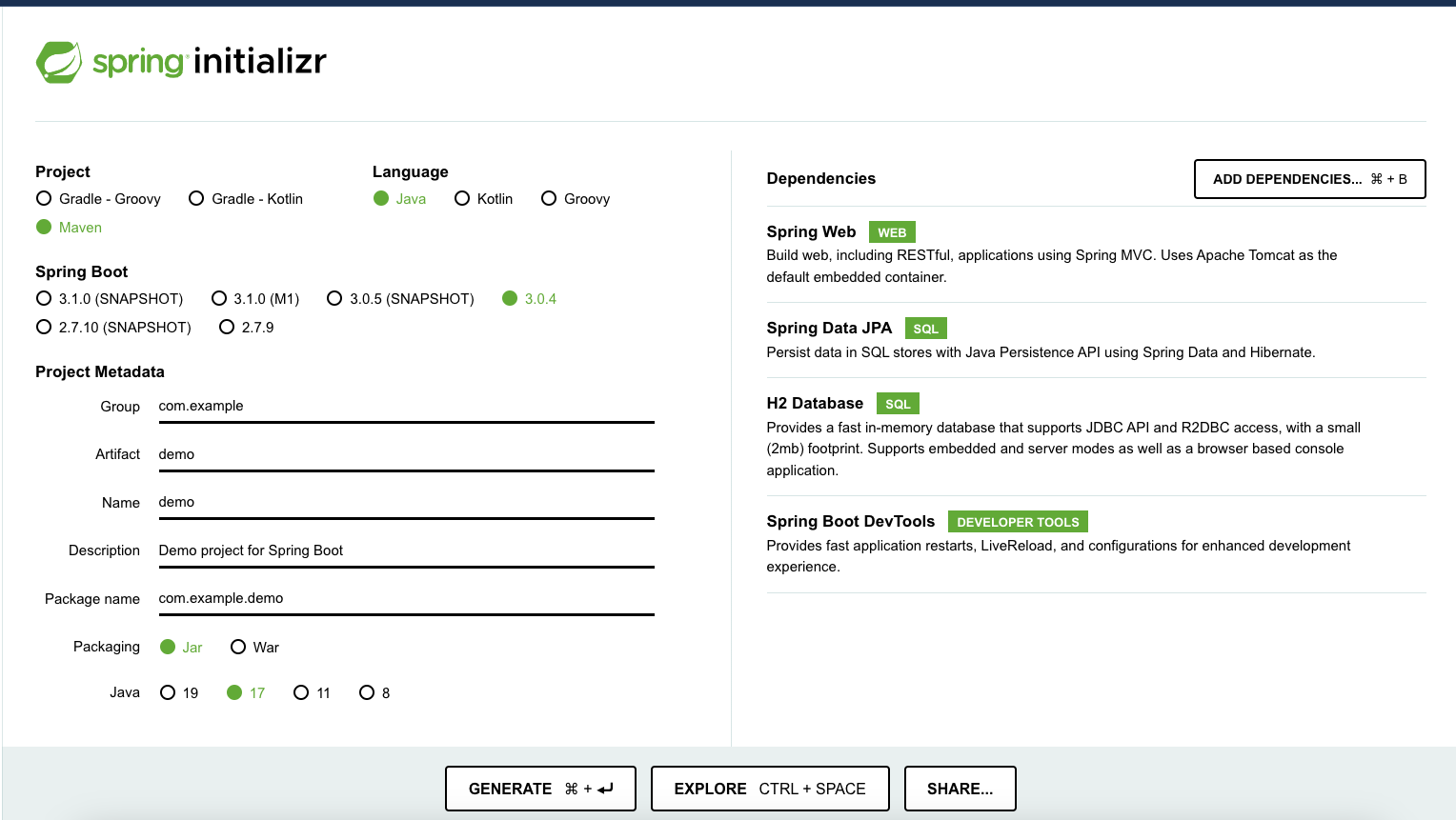
Creating the Project with Spring Initializr
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ is great tool to bootstrap your Spring Boot projects.

As shown in the image above, following steps have to be done
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following
- Choose
com.in28minutes.springboot.jpa.spring.data.rest.exampleas Group - Choose
spring-boot-2-jpa-spring-data-restas Artifact - Choose following dependencies
- Web
- JPA
- H2
- DevTools
- Rest Repositories
- Choose
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the project into Eclipse. File -> Import -> Existing Maven Project.
Do not forget to add the dependency on “Rest Repositories” i.e. Spring Boot Data Rest Starter.
Starter Projects in pom.xml
Below is the list of starter projects in pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Understanding Spring Boot Starter Data Rest
Below picture highlights some of the dependencies that are part of the imported Spring Boot project.

Key Question : How did all these dependencies come in?
Spring-boot-starter-jpa and spring-boot-starter-data-rest declare all of these dependencies. We obtain the following functionalities from a wide range of dependencies as soon as we include them in our project (pom.xml).
- Spring Data
- Spring Data Rest
- AOP
- Transaction Management
- JPA API
- JPA Implementation - Default Hibernate
- JDBC
Extract below shows some code from pom.xml of spring-boot-starter-data-rest.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-rest-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
Turn on H2 Console
H2 will be used as the database.
To see the data, H2 provides a web interface called H2 Console. Let’s activate the h2 console in the app. properties.
/src/main/resources/application.properties
# Enabling H2 Console
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
spring.data.jpa.repositories.bootstrap-mode=default
You may access H2 Console at http://localhost:8080/h2-console after reloading the application.
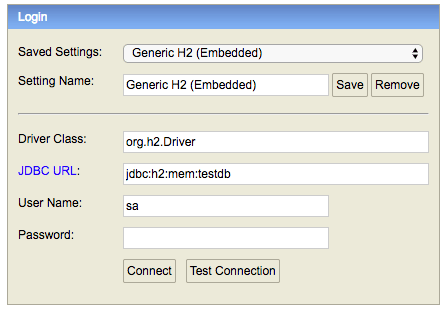
Tip - Make sure that you use
jdbc:h2:mem:testdbas JDBC URL.
When you provide the correct JDBC URL, you should see an empty schema when you click the Connect button.

Create Your First JPA Entity
The first thing to do is to build a JPA Entity. Let’s start with a basic Student Entity with a primary key id.
package com.in28minutes.springboot.jpa.spring.data.rest.example.student;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private String passportNumber;
Important things to note:
@Entity: Specifies that the class is an entity. This annotation is applied to the entity class.@Id: Specifies the primary key of an entity.@GeneratedValue: Provides for the specification of generation strategies for the values of primary keys.public Student(): Default constructor to make JPA Happy
You may access H2 Console at http://localhost:8080/h2-console after reloading the application.
On H2 Console, you will notice that a new table called’student’ is generated.
How did the Student table come to be?
Its because of Spring Boot Auto Configuration.
You can read more about auto configuration here - http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-auto-configuration
Let’s now add some information to the student table.
/src/main/resources/data.sql
insert into student
values(10001,'Ranga', 'E1234567');
insert into student
values(10002,'Ravi', 'A1234568');
After you refresh the application, you should see the following messages in the log showing that the sql files have been picked up.
Executing SQL script from URL [file:/in28Minutes/git/spring-boot-examples/spring-boot-2-jdbc-with-h2/target/classes/data.sql]
When you connect to H2 Console (http://localhost:8080/h2-console) after reloading the app, you will notice that the student table has been created and the data has been loaded.

Make a Spring Data Rest Repository class that exposes the Student API.
The code below demonstrates how to use the Spring Data Rest Repository to offer API for the Student resource.
/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/jpa/spring/data/rest/example/student/StudentDataRestRepository.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.jpa.spring.data.rest.example.student;
import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository;
import org.springframework.data.rest.core.annotation.RepositoryRestResource;
@RepositoryRestResource(path = "students", collectionResourceRel = "students")
public interface StudentDataRestRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Student, Long> {
}
RepositoryRestResource annotation is used to expose Spring Data Rest services
When the application reloads, you would see that there are a number of new statements in the console log.
Mapped "{[/ || ],methods=[GET],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.HttpEntity<org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryLinksResource> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryController.listRepositories()
Mapped "{[/{repository}],methods=[HEAD],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<?> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryEntityController.headCollectionResource(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.support.DefaultedPageable) throws org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
Mapped "{[/{repository}],methods=[POST],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<org.springframework.hateoas.ResourceSupport> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryEntityController.postCollectionResource(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResource,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResourceAssembler,java.lang.String) throws org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
Mapped "{[/{repository}/{id}],methods=[GET],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<org.springframework.hateoas.Resource<?>> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryEntityController.getItemResource(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,java.io.Serializable,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResourceAssembler,org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders) throws org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
Mapped "{[/{repository}/{id}],methods=[PUT],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<? extends org.springframework.hateoas.ResourceSupport> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryEntityController.putItemResource(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResource,java.io.Serializable,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResourceAssembler,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.support.ETag,java.lang.String) throws org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
Mapped "{[/{repository}/{id}],methods=[PATCH],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<org.springframework.hateoas.ResourceSupport> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryEntityController.patchItemResource(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResource,java.io.Serializable,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResourceAssembler,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.support.ETag,java.lang.String) throws org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.ResourceNotFoundException
Mapped "{[/{repository}/{id}],methods=[DELETE],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<?> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryEntityController.deleteItemResource(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,java.io.Serializable,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.support.ETag) throws org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.ResourceNotFoundException,org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
Mapped "{[/{repository}/search],methods=[GET],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositorySearchesResource org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositorySearchController.listSearches(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation)
Mapped "{[/{repository}/search/{search}],methods=[GET],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<?> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositorySearchController.executeSearch(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap<java.lang.String, java.lang.Object>,java.lang.String,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.support.DefaultedPageable,org.springframework.data.domain.Sort,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResourceAssembler,org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders)
Mapped "{[/{repository}/{id}/{property}/{propertyId}],methods=[GET],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<org.springframework.hateoas.ResourceSupport> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryPropertyReferenceController.followPropertyReference(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,java.io.Serializable,java.lang.String,java.lang.String,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResourceAssembler) throws java.lang.Exception
Mapped "{[/{repository}/{id}/{property}],methods=[GET],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<org.springframework.hateoas.ResourceSupport> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryPropertyReferenceController.followPropertyReference(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,java.io.Serializable,java.lang.String,org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.PersistentEntityResourceAssembler) throws java.lang.Exception
Mapped "{[/{repository}/{id}/{property}],methods=[PATCH || PUT || POST],consumes=[application/json || application/x-spring-data-compact+json || text/uri-list],produces=[application/hal+json || application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<? extends org.springframework.hateoas.ResourceSupport> org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RepositoryPropertyReferenceController.createPropertyReference(org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.RootResourceInformation,org.springframework.http.HttpMethod,org.springframework.hateoas.Resources<java.lang.Object>,java.io.Serializable,java.lang.String) throws java.lang.Exception
As we can see, Spring Data Rest exposes a variety of URIs with varying request methods. All of these resources will be examined in the next section.
RESTful APIs exposed by Spring Data Rest
Let’s have a look at some of the Resource URIs offered by Spring Data Rest in this section.
Spring Data Rest API - Get All Data for Resource
localhost:8080/students
- Request Method - GET
Response
{ "_embedded" : { "students" : [ { "name" : "Ranga", "passportNumber" : "E1234567", "_links" : { "self" : { "href" : "http://localhost:8080/students/10001" }, "student" : { "href" : "http://localhost:8080/students/10001" } } }, { "name" : "Ravi", "passportNumber" : "A1234568", "_links" : { "self" : { "href" : "http://localhost:8080/students/10002" }, "student" : { "href" : "http://localhost:8080/students/10002" } } } ] }, "_links" : { "self" : { "href" : "http://localhost:8080/students{?page,size,sort}", "templated" : true }, "profile" : { "href" : "http://localhost:8080/profile/students" } }, "page" : { "size" : 20, "totalElements" : 2, "totalPages" : 1, "number" : 0 } }
Notes:
_embedded- Details of all students are part of this JSON element._links- This section contains the links to other related resources - HATEOAS.page- This section contains the details of current page if we are using pagination. For example - http://localhost:8080/students?page=1 (0 indexed) will retrieve the second page of results. In this case, the page will be empty.- Support for sorting - http://localhost:8080/students?sort=passportNumber : Sort by passport number. Ravi would appear in the results before Ranga because his passport starts with “A”.
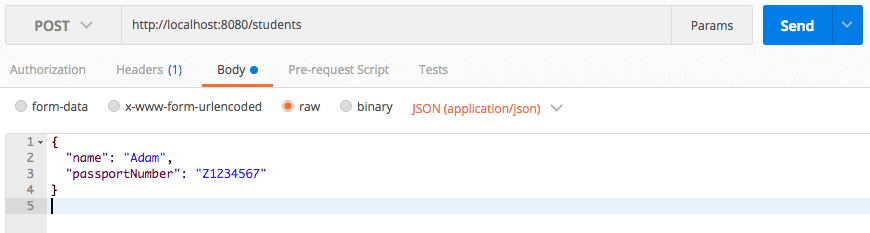
Student RESTful API - POST Method
- URI - http://localhost:8080/students
- Request Method - POST
- Content-Type - application/json
Request Body Content
{
"name": "Adam",
"passportNumber": "Z1234567"
}
When we execute the above request, a new student is created.
Response
{
"name": "Adam",
"passportNumber": "Z1234567",
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/students/1"
},
"student": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/students/1"
}
}
}
The response contains the URI to the created resource. Response Status - 201 CREATED.
Screenshot below shows a screenshot of executing the POST request using POSTMan

Student RESTful API - GET Method
- URI - http://localhost:8080/students
- Request Method - GET
When we execute the above request, details of a student are retrieved.
Response
{
"name": "Adam",
"passportNumber": "Z1234567",
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/students/1"
},
"student": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/students/1"
}
}
}
Student RESTful API - PUT Method
Used to update the details of a Student
- URI - http://localhost:8080/students/1
- Request Method - PUT
- Content-Type - application/json
Request Body Content
{
"name": "Adam",
"passportNumber": "Z12345678"
}
When we execute the above request, student details are updated.
Response
{
"name": "Adam",
"passportNumber": "Z12345678",
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/students/1"
},
"student": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/students/1"
}
}
}
The response contains the URI to the updated resource.
Student RESTful API - Delete Method
- URI - http://localhost:8080/students/1
- Request Method - DELETE
Student 1 is deleted.
ALPS REST API for Resource Semantics
ALPS is a data format for defining concise representations of application-level semantics, equivalent to HTML microformats in complexity. An ALPS document can be used as a profile to describe the application semantics of a document that uses an application-independent media type (such as HTML, HAL, Collection+JSON, Siren, and so on). This improves profile document reusability across media formats.
- URI - http://localhost:8080/profile/students
Response
{
"alps": {
"version": "1.0",
"descriptors": [
{
"id": "student-representation",
"href": "http://localhost:8080/profile/students",
"descriptors": [
{
"name": "name",
"type": "SEMANTIC"
},
{
"name": "passportNumber",
"type": "SEMANTIC"
}
]
},
{
"id": "get-students",
"name": "students",
"type": "SAFE",
"rt": "#student-representation",
"descriptors": [
{
"name": "page",
"doc": {
"value": "The page to return.",
"format": "TEXT"
},
"type": "SEMANTIC"
},
{
"name": "size",
"doc": {
"value": "The size of the page to return.",
"format": "TEXT"
},
"type": "SEMANTIC"
},
{
"name": "sort",
"doc": {
"value": "The sorting criteria to use to calculate the content of the page.",
"format": "TEXT"
},
"type": "SEMANTIC"
}
]
},
{
"id": "create-students",
"name": "students",
"type": "UNSAFE",
"rt": "#student-representation"
},
{
"id": "update-student",
"name": "student",
"type": "IDEMPOTENT",
"rt": "#student-representation"
},
{
"id": "delete-student",
"name": "student",
"type": "IDEMPOTENT",
"rt": "#student-representation"
},
{
"id": "get-student",
"name": "student",
"type": "SAFE",
"rt": "#student-representation"
},
{
"id": "patch-student",
"name": "student",
"type": "UNSAFE",
"rt": "#student-representation"
}
]
}
}
Other Features
Some of the other features of spring data rest include
- Paging and Sorting
- Customizing Serialization with Jackson’s ObjectMapper
- Projections
- Validation
- Security
- CORS Configurability
Refer to official documentation of Spring Data Rest for more details - https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/rest/docs/3.0.2.RELEASE/reference/html/