This guide will introduce you to profiles and help you understand how to use profiles with the various application configuration options that are present in Spring Boot.
You will learn
- What is application configuration?
- What is a profile?
- How do you define beans for a specific profile?
- How do you create application configuration for a specific profile?
- How do you have different configuration for different environments?
Need for Application Configuration
Configuration for applications vary from one environment to another
- You would want to connect to a different database or queues
- You would want to connect with different services
- You would want to configure less logging in production
- You might want to have different custom configuration
Need for Profiles
Enterprise application development is complex. You have multiple environments
- Dev
- QA
- Stage
- Production
You want to have different application configuration in each of the environments.
Profiles help to have different application configuration for different environments.
Spring and Spring Boot provide features where you can specify
- What is the configuration for various environments in different profiles?
- Set the active profile for a specific environment.
Spring Boot would pick up the application configuration based on the active profile that is set in a specific environment.
Project Code Structure
Following screen shot shows the structure of the project we will create.

A few details:
- SpringBootTutorialBasicsConfigurationApplication.java - The Spring Boot Application class generated with Spring Initializer. This class acts as the launching point for application. In this example, a few profile based beans are also created in the Application class.
pom.xml- Contains all the dependencies needed to build this project.BasicConfiguration.java- We will use this component to define application configuration using @ConfigurationPropertiesWelcomeResource.java- Example of a resource using @Valueapplication.properties- Configuration for application. Active profile is set in application.properties in this exampleapplication-dev.properties- Configuration Overrides for dev profileapplication-prod.properties- Configuration Overrides for prod profile
Tools you will need
- Maven 3.0+ is your build tool
- Your favorite IDE. We use Eclipse.
- JDK 1.8+
Complete Maven Project With Code Examples
Our Github repository has all the code examples - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-examples/tree/master/spring-boot-tutorial-basics-configuration
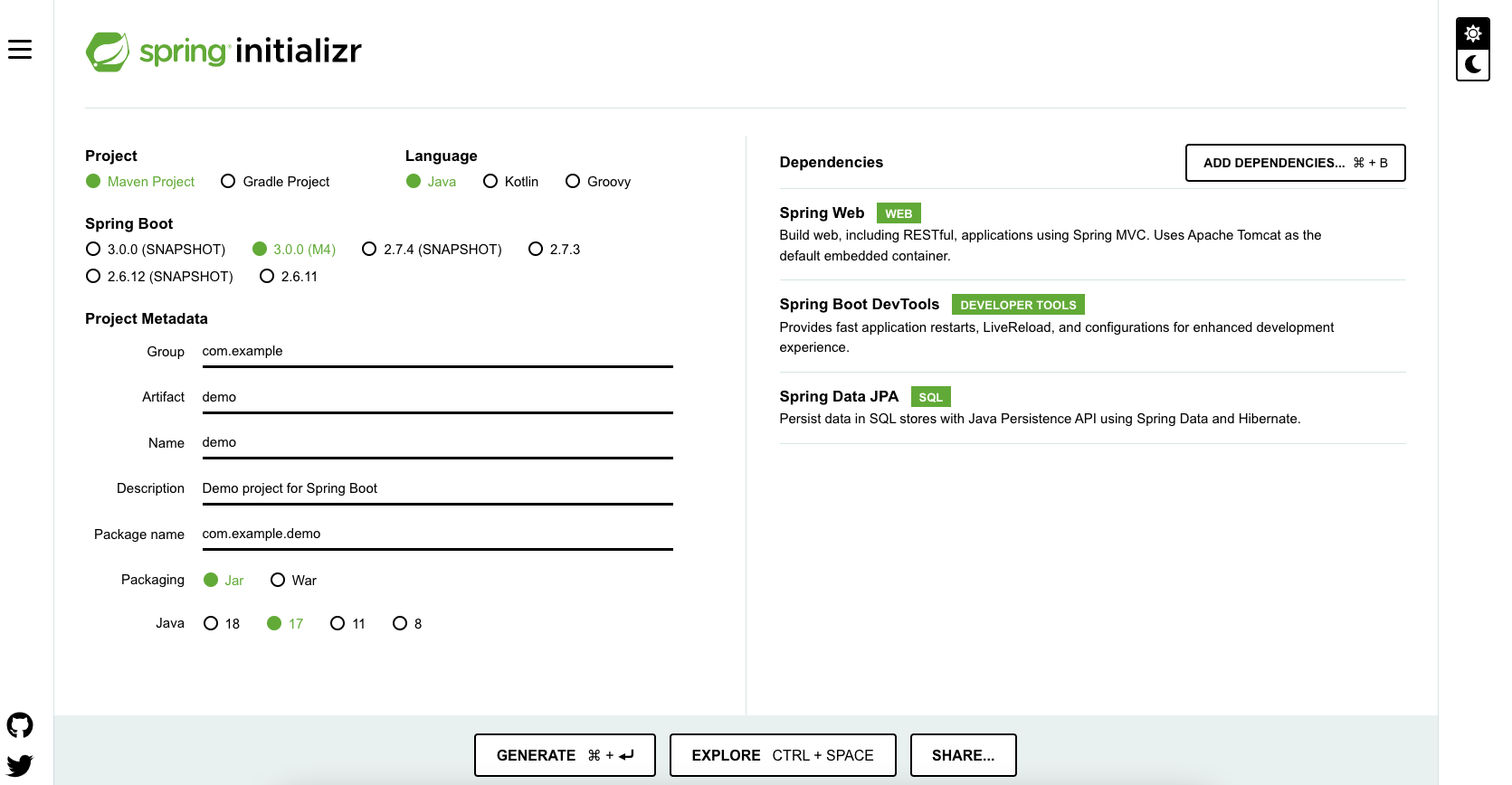
Bootstrapping with Spring Initializr
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ is great tool to bootstrap your Spring Boot projects.
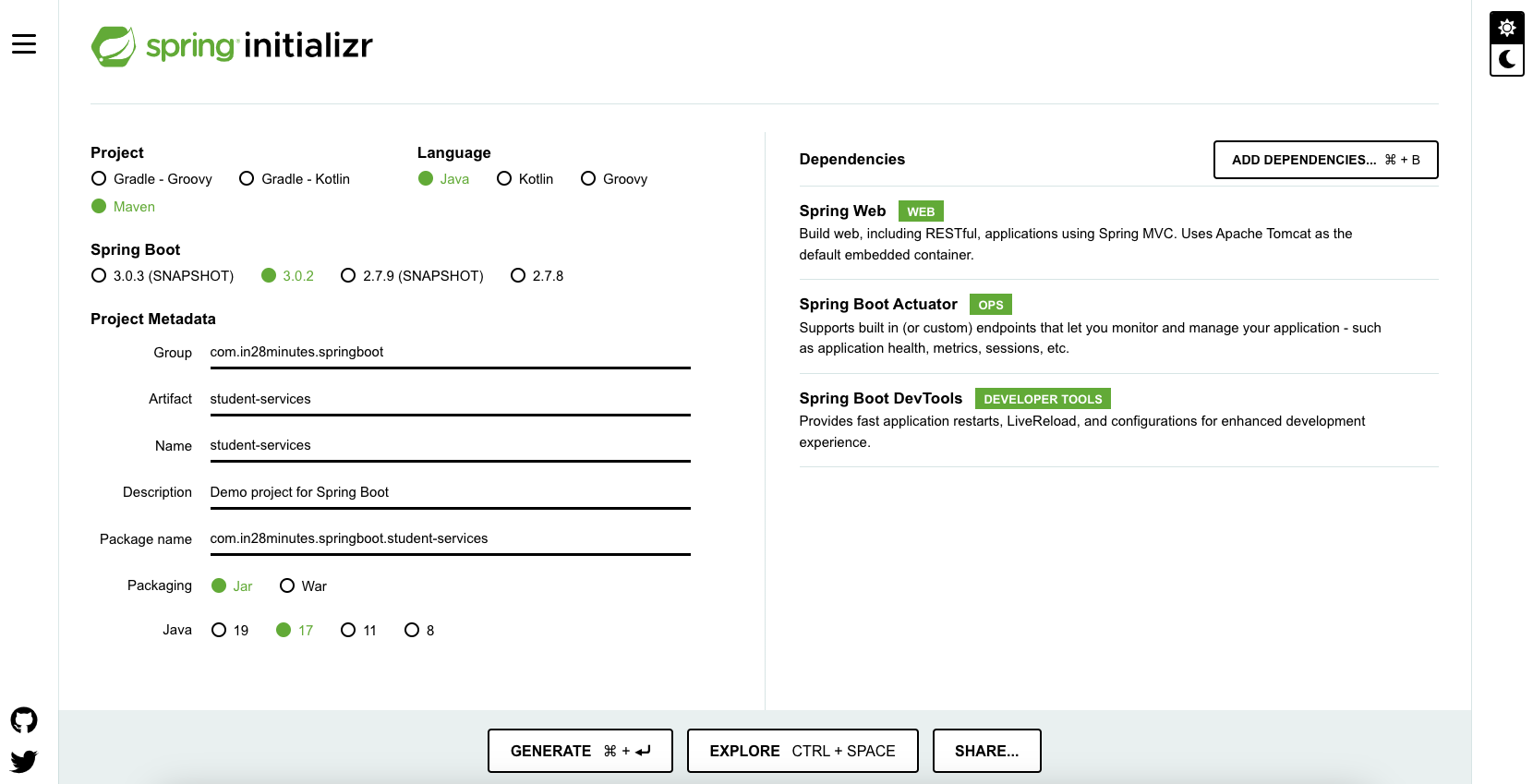

As shown in the image above, following steps have to be done
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following
- Choose
com.in28minutes.springboot.tutorial.basics.application.configurationas Group - Choose
spring-boot-tutorial-basics-configurationas Artifact - Choose following dependencies
- Web
- DevTools
- Choose
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the project into Eclipse. File -> Import -> Existing Maven Project.
Set up a Quick Example to illustrate Profiles
Lets create a simple resource to expose application configuration using @Value.
@RestController
public class WelcomeResource {
@Value("${welcome.message}")
private String welcomeMessage;
@GetMapping("/welcome")
public String retrieveWelcomeMessage() {
// Complex Method
return welcomeMessage;
}
}
Value for welcome message can be configured in application.properties.
welcome.message=Welcome message from property file! Welcome to in28Minutes
When you launch http://localhost:8080/welcome, you would see a page with this message
Welcome message from property file! Welcome to in28Minutes
Let’s define another simple resource specifying application configuration using @ConfigurationProperties.
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("basic")
public class BasicConfiguration {
private boolean value;
private String message;
private int number;
//GETTERS AND SETTERS
}
We would need to use the BasicConfiguration in a service to expose the values
@Autowired
private BasicConfiguration configuration;
@RequestMapping("/dynamic-configuration")
public Map dynamicConfiguration() {
// Not the best practice to use a map to store differnt types!
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("message", configuration.getMessage());
map.put("number", configuration.getNumber());
map.put("key", configuration.isValue());
return map;
}
When you browse to http://localhost:8080/dynamic-configuration, you see the following response.
{"number":100,"message":"Dynamic Message","key":true}
The above example is explained step by step in more detail in the Application Configuration article - http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-application-configuration
Using Profiles to configure environment specific configuration
Profile is nothing but a key to identify an environment.
In this example, we will use two profiles
- dev
- prod
The default application configuration is present in application.properties. Let’s consider an example.
application.properties
logging.level.org.springframework.web.servlet: DEBUG
app.name=in28Minutes
welcome.message=Welcome message from property file! Welcome to ${app.name}
basic.value= true
basic.message= Dynamic Message
basic.number= 100
We would want to customize the application.properties for DEV profile. We would need to create a file with name application-dev.properties and override the properties that we would want to customize.
application-dev.properties
welcome.message=Welcome message from property file! Welcome to ${app.name} in DEV
basic.message: Dynamic Message in DEV
Similarly you can configure properties for prod profile.
application-prod.properties
welcome.message=Welcome message from property file! Welcome to ${app.name} in Prod
basic.message: Dynamic Message in Prod
Setting Active Profile
Once you have profile specific configuration, you would need to set the active profile in an environment.
There are multiple ways of doing this
- Using -Dspring.profiles.active=prod in VM Arguments
- Use
spring.profiles.active=prodin application.properties
In this example let’s set it in application.properties. Lets add another property to application.properties
spring.profiles.active=dev
When you restart the application, you would see that the dev profile is active.
otTutorialBasicsConfigurationApplication : The following profiles are active: dev
Look at the response from services
http://localhost:8080/welcome
Welcome message from property file! Welcome to in28Minutes in DEV
http://localhost:8080/dynamic-configuration
{"number":100,"message":"Dynamic Message in DEV","key":true}
You can see that the configuration for dev profile is being picked up by Spring Boot.
Configuring Profile Specific Beans
You can take this one step further and configure profile specific beans that are created only in specific profiles.
Let’s add this to SpringBootTutorialBasicsConfigurationApplication.java
@Profile("dev")
@Bean
public String devBean() {
return "dev";
}
@Profile("qa")
@Bean
public String qaBean() {
return "qa";
}
@Profile("prod")
@Bean
public String prodBean() {
return "prod";
}
Using @Profile annotation we can indicate the active profile in which a specific bean should be created.
To test this let’s further enhance SpringBootTutorialBasicsConfigurationApplication.
Let’s print the name of all the beans that are loaded.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication
.run(SpringBootTutorialBasicsConfigurationApplication.class, args);
for (String name : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
We are currently using dev profile
spring.profiles.active=dev
When you reload the application, you would see the following in the log
devBean
You would see that the devBean is created. However, the beans shown below are not created because those profiles are not active.
@Profile("qa")
@Bean
public String qaBean() {
return "qa";
}
@Profile("prod")
@Bean
public String prodBean() {
return "prod";
}
Complete Maven Project With Code Examples
Our Github repository has all the code examples - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-examples/tree/master/spring-boot-tutorial-basics-configuration